The manufacturing of concrete blocks is a precise and highly-engineered industrial process. From raw material preparation to the final curing, each step is optimized for efficiency, strength, and consistency. This guide explores the complete industrial process of concrete block manufacturing, offering insights into the technology and machinery that make it all possible.
The Concrete Block Manufacturing Process
The production of concrete blocks can be broken down into three main stages: material preparation and mixing, molding and compaction, and curing and finishing.
1. Material Preparation and Mixing
The journey of a concrete block begins with its core ingredients: cement, sand, gravel, and water. These materials are carefully selected and proportioned to ensure the final product meets strict quality standards. The process starts with batching, where raw materials are precisely weighed. Cement is typically stored in large silos, while aggregates like sand and gravel are moved by conveyor belts to a weigh batcher. This precision is critical for the structural integrity of the blocks.
Once batched, the dry materials are transferred to a stationary mixer, often a planetary or pan mixer, for a thorough blending. After a few minutes of dry mixing, water is introduced. The entire mixing cycle usually lasts between six to eight minutes, resulting in a homogenous concrete mixture ready for the next stage.
2. Molding and Compaction
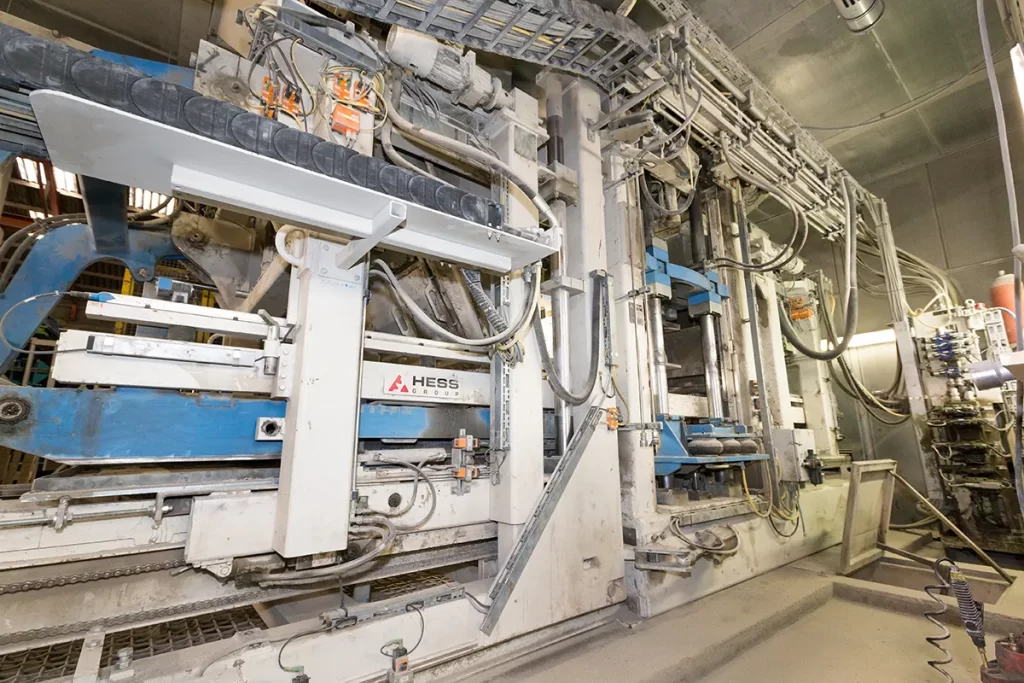
The heart of the concrete block manufacturing process is the block-making machine. The prepared concrete mix is transported via conveyor to a hopper, which feeds the machine’s mold. Modern block-making machines utilize vibro-press technology, a combination of high-pressure and intense vibration. This powerful combination compacts the concrete, forcing it into the shape of the mold and creating a dense, strong block. These machines are also known as non-burning block machines because they don’t require firing or baking to harden the blocks.
After molding, the freshly formed blocks, still on steel pallets, are moved by a conveyor to an automated stacker. The stacker arranges the blocks onto curing racks, preparing them for the final stage of the process.
3. Curing and Finishing
Curing is a crucial step that allows the cement to hydrate, a chemical reaction that gives the concrete its strength, durability, and water-tightness. The racks of blocks are moved into a curing kiln, where the environment is carefully controlled. While there are various methods, low-pressure steam curing is common. The blocks are gradually heated with steam, allowed to soak in the warm, moist air, and then dried. This accelerated curing process can take up to 24 hours.
After curing, the blocks are unstacked and moved to a cuber, which arranges them into standardized cubes for easy storage and transportation. The steel pallets are then cleaned and returned to the block-making machine, ready for the next cycle.
The European Concrete Block Market
The concrete block industry is a significant part of the European construction sector. The European cement and concrete industry directly employed 36,282 people in the EU27 in 2023 [1]. The market itself is substantial, with the European concrete block market valued at USD $12.5 billion in 2024 [2]. This demonstrates the continued importance and demand for concrete blocks in construction projects across the continent.
Your Partner in Concrete Block Production
For businesses involved in concrete block manufacturing, having the right equipment is essential. At JOSEF RATH GmbH, we specialize in providing high-quality new and used concrete block machines and related equipment. With decades of international experience, we offer a wide range of machinery to suit your production needs, including:
•Stationary Machines: High-capacity machines for large-scale production.
•Mobile Machines: Flexible solutions for on-site production.
•Used Machines: Cost-effective options for expanding or upgrading your operations.
•Concrete Molds: A variety of molds to produce different types of blocks.
We are committed to providing our customers with reliable machinery and expert support. Contact us today to learn how we can help you with your concrete block production needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the main raw materials for concrete blocks?
The primary raw materials are cement, sand (fine aggregate), gravel or crushed stone (coarse aggregate), and water.
What is vibro-press technology?
Vibro-press technology is a method used in modern block-making machines that combines high pressure and vibration to compact concrete into dense, strong blocks.
How long does it take to cure concrete blocks?
The curing process can take up to 24 hours, depending on the method used. Accelerated curing methods, like steam curing, are often used in industrial production.
What types of machines are used in concrete block production?
The main types of machines are stationary and mobile (or egg-layer) block-making machines. Stationary machines are ideal for large-scale, continuous production, while mobile machines offer flexibility for smaller or remote projects.
